Make Service Area Layer Tool
أداة إنشاء طبقة منطقة الخدمة
ArcMap ArcGIS
How to use Make Service Area Layer Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
كيفية استخدام أداة إنشاء طبقة منطقة الخدمة ؟؟
Path
to access the toolمسار الوصول الى الأداة
:
Make
Service Area Layer Tool, Analysis Toolset, Network
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Make Service Area Layer
Makes a service area
network analysis layer and sets its analysis properties. A service area
analysis layer is useful in determining the area of accessibility within a
given cutoff cost from a facility location.
يقوم بإنشاء طبقة تحليل شبكة منطقة الخدمة وتعيين
خصائص التحليل الخاصة بها. تُعد طبقة تحليل منطقة الخدمة مفيدة في تحديد منطقة
إمكانية الوصول ضمن تكلفة قطع معينة من موقع المنشأة.
1.
Input Analysis Network أدخل تحليل
الشبكة
The network dataset on
which the service area analysis will be performed.
مجموعة بيانات الشبكة التي سيتم إجراء تحليل منطقة
الخدمة عليها.
Output
Layer Name
Name of the service area network analysis layer to create.
Impedance
Attribute
The cost attribute to be used as impedance in the analysis.
Travel
From or To Facility (optional)
Specifies the direction of travel to or from the facilities.
· TRAVEL_FROM—The service area is created in the direction away from the
facilities.
· TRAVEL_TO—The service area is created in the direction towards the
facilities.
Using this option can result in different service areas on a network with
one-way restrictions and having different impedances based on direction of
travel. The service area for a pizza delivery store, for example, should be
created away from the facility, whereas the service area of a hospital should
be created toward the facility.
Default
Break Values (optional)
Default impedance values indicating the extent of the service area to be
calculated. The default can be overridden by specifying the break value on the
facilities.
Multiple polygon breaks can be set to create concentric service areas. For
instance, to find 2-, 3-, and 5-minute service areas for the same facility,
specify "2 3 5" as the value for the Default break values parameter
(the numbers 2, 3, and 5 should be separated by a space).
Time of
Day (optional)
The time to depart from or arrive at the facilities of the service area
layer. The interpretation of this value as a depart or arrive time depends on
whether travel is away from or toward the facilities.
· It represents the departure time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_FROM.
· It represents the arrival time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_TO.
If you have chosen a traffic-based impedance attribute, the solution will
be generated given dynamic traffic conditions at the time of day specified
here. A date and time can be specified as 5/14/2012 10:30 AM.
Instead of using a particular date, a day of the week can be specified
using the following dates:
· Today—12/30/1899
· Sunday—12/31/1899
· Monday—1/1/1900
· Tuesday—1/2/1900
· Wednesday—1/3/1900
· Thursday—1/4/1900
· Friday—1/5/1900
· Saturday—1/6/1900
For
example, to specify that travel should begin at 5:00 p.m. on Tuesday, specify
the parameter value as 1/2/1900 5:00 PM.
Repeatedly solving the same analysis, but using different Time of Day
values, allows you to see how a facility's reach changes over time. For
instance, the five-minute service area around a fire station may start out
large in the early morning, diminish during the morning rush hour, grow in the
late morning, and so on throughout the day.
Accumulators
(optional)
A list of cost attributes to be accumulated during analysis. These
accumulation attributes are purely for reference; the solver only uses the cost
attribute specified by the Impedance Attribute parameter to calculate the
route.
For each cost attribute that is accumulated, a Total_[Impedance] property
is added to the routes that are output by the solver.
Use
Hierarchy in Analysis (optional)
· Checked—Use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Using a hierarchy
results in the solver preferring higher-order edges to lower-order edges.
Hierarchical solves are faster, and they can be used to simulate the preference
of a driver who chooses to travel on freeways over local roads when
possible—even if that means a longer trip. This option is enabled only if the
input network dataset has a hierarchy attribute.
· Unchecked—Do not use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Not using a
hierarchy yields a service area measured along all edges of the network dataset
regardless of hierarchy level.
The parameter is disabled if a hierarchy attribute is not defined on the
network dataset used to perform the analysis.
Line Type
(optional)
Specifies the type of lines to be generated based on the service area
analysis. Selecting the True Lines or True lines with measures option for large
service areas will increase the amount of memory consumed by the analysis.
· NO_LINES—Do not generate lines. This is the default.
· TRUE_LINES—Lines are generated without measures.
· TRUE_LINES_WITH_MEASURES—Lines are generated with measures. The measure
values are generated based on the impedance value on each end of the edge with
the intermediate vertices interpolated. Do not use this option if faster
performance is desired.
Overlap
Lines (optional)
Determines if overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines
are computed.
· Checked—Include a separate line feature for each facility when the
facilities have service area lines that are coincident.
· Unchecked—Include each service area line at most once and associate it
with its closest (least impedance) facility.
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
2.
Output Layer Name اسم طبقة الإخراج
Name of the service area
network analysis layer to create.
اسم طبقة تحليل شبكة منطقة الخدمة المراد إنشاؤها.
Impedance
Attribute
The cost attribute to be used as impedance in the analysis.
Travel
From or To Facility (optional)
Specifies the direction of travel to or from the facilities.
· TRAVEL_FROM—The service area is created in the direction away from the
facilities.
· TRAVEL_TO—The service area is created in the direction towards the
facilities.
Using this option can result in different service areas on a network with
one-way restrictions and having different impedances based on direction of
travel. The service area for a pizza delivery store, for example, should be
created away from the facility, whereas the service area of a hospital should
be created toward the facility.
Default
Break Values (optional)
Default impedance values indicating the extent of the service area to be
calculated. The default can be overridden by specifying the break value on the
facilities.
Multiple polygon breaks can be set to create concentric service areas. For
instance, to find 2-, 3-, and 5-minute service areas for the same facility,
specify "2 3 5" as the value for the Default break values parameter
(the numbers 2, 3, and 5 should be separated by a space).
Time of
Day (optional)
The time to depart from or arrive at the facilities of the service area
layer. The interpretation of this value as a depart or arrive time depends on
whether travel is away from or toward the facilities.
· It represents the departure time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_FROM.
· It represents the arrival time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_TO.
If you have chosen a traffic-based impedance attribute, the solution will
be generated given dynamic traffic conditions at the time of day specified
here. A date and time can be specified as 5/14/2012 10:30 AM.
Instead of using a particular date, a day of the week can be specified
using the following dates:
· Today—12/30/1899
· Sunday—12/31/1899
· Monday—1/1/1900
· Tuesday—1/2/1900
· Wednesday—1/3/1900
· Thursday—1/4/1900
· Friday—1/5/1900
· Saturday—1/6/1900
For
example, to specify that travel should begin at 5:00 p.m. on Tuesday, specify
the parameter value as 1/2/1900 5:00 PM.
Repeatedly solving the same analysis, but using different Time of Day
values, allows you to see how a facility's reach changes over time. For
instance, the five-minute service area around a fire station may start out
large in the early morning, diminish during the morning rush hour, grow in the
late morning, and so on throughout the day.
Accumulators
(optional)
A list of cost attributes to be accumulated during analysis. These
accumulation attributes are purely for reference; the solver only uses the cost
attribute specified by the Impedance Attribute parameter to calculate the
route.
For each cost attribute that is accumulated, a Total_[Impedance] property
is added to the routes that are output by the solver.
Use
Hierarchy in Analysis (optional)
· Checked—Use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Using a hierarchy
results in the solver preferring higher-order edges to lower-order edges.
Hierarchical solves are faster, and they can be used to simulate the preference
of a driver who chooses to travel on freeways over local roads when
possible—even if that means a longer trip. This option is enabled only if the
input network dataset has a hierarchy attribute.
· Unchecked—Do not use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Not using a
hierarchy yields a service area measured along all edges of the network dataset
regardless of hierarchy level.
The parameter is disabled if a hierarchy attribute is not defined on the
network dataset used to perform the analysis.
Line Type
(optional)
Specifies the type of lines to be generated based on the service area
analysis. Selecting the True Lines or True lines with measures option for large
service areas will increase the amount of memory consumed by the analysis.
· NO_LINES—Do not generate lines. This is the default.
· TRUE_LINES—Lines are generated without measures.
· TRUE_LINES_WITH_MEASURES—Lines are generated with measures. The measure
values are generated based on the impedance value on each end of the edge with
the intermediate vertices interpolated. Do not use this option if faster
performance is desired.
Overlap
Lines (optional)
Determines if overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines
are computed.
· Checked—Include a separate line feature for each facility when the
facilities have service area lines that are coincident.
· Unchecked—Include each service area line at most once and associate it
with its closest (least impedance) facility.
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description of
its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
3.
Impedance Attribute جدول المعاوقة
The cost attribute to be
used as impedance in the analysis.
جدول التكلفة التي سيتم استخدامها كمعاوقة في
التحليل.
Travel
From or To Facility (optional)
Specifies the direction of travel to or from the facilities.
· TRAVEL_FROM—The service area is created in the direction away from the
facilities.
· TRAVEL_TO—The service area is created in the direction towards the
facilities.
Using this option can result in different service areas on a network with
one-way restrictions and having different impedances based on direction of
travel. The service area for a pizza delivery store, for example, should be
created away from the facility, whereas the service area of a hospital should
be created toward the facility.
Default
Break Values (optional)
Default impedance values indicating the extent of the service area to be
calculated. The default can be overridden by specifying the break value on the
facilities.
Multiple polygon breaks can be set to create concentric service areas. For
instance, to find 2-, 3-, and 5-minute service areas for the same facility,
specify "2 3 5" as the value for the Default break values parameter
(the numbers 2, 3, and 5 should be separated by a space).
Time of
Day (optional)
The time to depart from or arrive at the facilities of the service area
layer. The interpretation of this value as a depart or arrive time depends on
whether travel is away from or toward the facilities.
· It represents the departure time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_FROM.
· It represents the arrival time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_TO.
If you have chosen a traffic-based impedance attribute, the solution will
be generated given dynamic traffic conditions at the time of day specified
here. A date and time can be specified as 5/14/2012 10:30 AM.
Instead of using a particular date, a day of the week can be specified
using the following dates:
· Today—12/30/1899
· Sunday—12/31/1899
· Monday—1/1/1900
· Tuesday—1/2/1900
· Wednesday—1/3/1900
· Thursday—1/4/1900
· Friday—1/5/1900
· Saturday—1/6/1900
For
example, to specify that travel should begin at 5:00 p.m. on Tuesday, specify
the parameter value as 1/2/1900 5:00 PM.
Repeatedly solving the same analysis, but using different Time of Day
values, allows you to see how a facility's reach changes over time. For
instance, the five-minute service area around a fire station may start out
large in the early morning, diminish during the morning rush hour, grow in the
late morning, and so on throughout the day.
Accumulators
(optional)
A list of cost attributes to be accumulated during analysis. These
accumulation attributes are purely for reference; the solver only uses the cost
attribute specified by the Impedance Attribute parameter to calculate the
route.
For each cost attribute that is accumulated, a Total_[Impedance] property
is added to the routes that are output by the solver.
Use
Hierarchy in Analysis (optional)
· Checked—Use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Using a hierarchy
results in the solver preferring higher-order edges to lower-order edges.
Hierarchical solves are faster, and they can be used to simulate the preference
of a driver who chooses to travel on freeways over local roads when
possible—even if that means a longer trip. This option is enabled only if the
input network dataset has a hierarchy attribute.
· Unchecked—Do not use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Not using a
hierarchy yields a service area measured along all edges of the network dataset
regardless of hierarchy level.
The parameter is disabled if a hierarchy attribute is not defined on the
network dataset used to perform the analysis.
Line Type
(optional)
Specifies the type of lines to be generated based on the service area
analysis. Selecting the True Lines or True lines with measures option for large
service areas will increase the amount of memory consumed by the analysis.
· NO_LINES—Do not generate lines. This is the default.
· TRUE_LINES—Lines are generated without measures.
· TRUE_LINES_WITH_MEASURES—Lines are generated with measures. The measure
values are generated based on the impedance value on each end of the edge with
the intermediate vertices interpolated. Do not use this option if faster
performance is desired.
Overlap
Lines (optional)
Determines if overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines
are computed.
· Checked—Include a separate line feature for each facility when the
facilities have service area lines that are coincident.
· Unchecked—Include each service area line at most once and associate it
with its closest (least impedance) facility.
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
4.
Travel from or To Facility (optional) السفر من أو إلى مرفق (اختياري)
Specifies the direction
of travel to or from the facilities.
يحدد اتجاه السفر من وإلى المرافق.
• TRAVEL_FROM - يتم إنشاء منطقة الخدمة في الاتجاه بعيدًا عن المرافق.
• TRAVEL_TO - يتم إنشاء منطقة الخدمة في الاتجاه نحو المرافق.
يمكن أن يؤدي استخدام هذا الخيار إلى مناطق خدمة
مختلفة على شبكة ذات قيود أحادية الاتجاه ولها مقاومة مختلفة بناءً على اتجاه
السفر. يجب إنشاء منطقة الخدمة لمتجر توصيل البيتزا ، على سبيل المثال ، بعيدًا عن
المنشأة ، بينما يجب إنشاء منطقة الخدمة الخاصة بالمستشفى تجاه المنشأة.
Default
Break Values (optional)
Default impedance values indicating the extent of the service area to be
calculated. The default can be overridden by specifying the break value on the
facilities.
Multiple polygon breaks can be set to create concentric service areas. For
instance, to find 2-, 3-, and 5-minute service areas for the same facility,
specify "2 3 5" as the value for the Default break values parameter
(the numbers 2, 3, and 5 should be separated by a space).
Time of
Day (optional)
The time to depart from or arrive at the facilities of the service area
layer. The interpretation of this value as a depart or arrive time depends on
whether travel is away from or toward the facilities.
· It represents the departure time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_FROM.
· It represents the arrival time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_TO.
If you have chosen a traffic-based impedance attribute, the solution will
be generated given dynamic traffic conditions at the time of day specified
here. A date and time can be specified as 5/14/2012 10:30 AM.
Instead of using a particular date, a day of the week can be specified
using the following dates:
· Today—12/30/1899
· Sunday—12/31/1899
· Monday—1/1/1900
· Tuesday—1/2/1900
· Wednesday—1/3/1900
· Thursday—1/4/1900
· Friday—1/5/1900
· Saturday—1/6/1900
For
example, to specify that travel should begin at 5:00 p.m. on Tuesday, specify
the parameter value as 1/2/1900 5:00 PM.
Repeatedly solving the same analysis, but using different Time of Day
values, allows you to see how a facility's reach changes over time. For
instance, the five-minute service area around a fire station may start out
large in the early morning, diminish during the morning rush hour, grow in the
late morning, and so on throughout the day.
Accumulators
(optional)
A list of cost attributes to be accumulated during analysis. These
accumulation attributes are purely for reference; the solver only uses the cost
attribute specified by the Impedance Attribute parameter to calculate the
route.
For each cost attribute that is accumulated, a Total_[Impedance] property
is added to the routes that are output by the solver.
Use
Hierarchy in Analysis (optional)
· Checked—Use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Using a hierarchy
results in the solver preferring higher-order edges to lower-order edges.
Hierarchical solves are faster, and they can be used to simulate the preference
of a driver who chooses to travel on freeways over local roads when
possible—even if that means a longer trip. This option is enabled only if the
input network dataset has a hierarchy attribute.
· Unchecked—Do not use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Not using a
hierarchy yields a service area measured along all edges of the network dataset
regardless of hierarchy level.
The parameter is disabled if a hierarchy attribute is not defined on the
network dataset used to perform the analysis.
Line Type
(optional)
Specifies the type of lines to be generated based on the service area
analysis. Selecting the True Lines or True lines with measures option for large
service areas will increase the amount of memory consumed by the analysis.
· NO_LINES—Do not generate lines. This is the default.
· TRUE_LINES—Lines are generated without measures.
· TRUE_LINES_WITH_MEASURES—Lines are generated with measures. The measure
values are generated based on the impedance value on each end of the edge with
the intermediate vertices interpolated. Do not use this option if faster
performance is desired.
Overlap
Lines (optional)
Determines if overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines
are computed.
· Checked—Include a separate line feature for each facility when the
facilities have service area lines that are coincident.
· Unchecked—Include each service area line at most once and associate it
with its closest (least impedance) facility.
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
5.
Default Break Values (optional) قيم
الفاصل الافتراضية (اختياري)
Default impedance values
indicating the extent of the service area to be calculated. The default can be
overridden by specifying the break value on the facilities.
Multiple polygon breaks
can be set to create concentric service areas. For instance, to find 2-, 3-,
and 5-minute service areas for the same facility, specify "2 3 5" as
the value for the Default break values parameter (the numbers 2, 3, and 5
should be separated by a space).
تشير قيم المعاوقة الافتراضية إلى مدى منطقة
الخدمة المطلوب حسابها. يمكن تجاوز القيمة الافتراضية عن طريق تحديد قيمة الفاصل
على المرافق.
يمكن تعيين فواصل متعددة الأضلاع لإنشاء مناطق
خدمة متحدة المركز. على سبيل المثال ، للعثور على مناطق خدمة مدتها 2 و 3 و 5
دقائق لنفس المنشأة ، حدد "2 3 5" كقيمة لمعلمة قيم الفاصل الافتراضية
(يجب فصل الأرقام 2 و 3 و 5 بواسطة مساحة).
Time of
Day (optional)
The time to depart from or arrive at the facilities of the service area
layer. The interpretation of this value as a depart or arrive time depends on
whether travel is away from or toward the facilities.
· It represents the departure time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_FROM.
· It represents the arrival time if Travel From or To Facility is set to
TRAVEL_TO.
If you have chosen a traffic-based impedance attribute, the solution will
be generated given dynamic traffic conditions at the time of day specified
here. A date and time can be specified as 5/14/2012 10:30 AM.
Instead of using a particular date, a day of the week can be specified
using the following dates:
· Today—12/30/1899
· Sunday—12/31/1899
· Monday—1/1/1900
· Tuesday—1/2/1900
· Wednesday—1/3/1900
· Thursday—1/4/1900
· Friday—1/5/1900
· Saturday—1/6/1900
For
example, to specify that travel should begin at 5:00 p.m. on Tuesday, specify
the parameter value as 1/2/1900 5:00 PM.
Repeatedly solving the same analysis, but using different Time of Day
values, allows you to see how a facility's reach changes over time. For
instance, the five-minute service area around a fire station may start out
large in the early morning, diminish during the morning rush hour, grow in the
late morning, and so on throughout the day.
Accumulators
(optional)
A list of cost attributes to be accumulated during analysis. These
accumulation attributes are purely for reference; the solver only uses the cost
attribute specified by the Impedance Attribute parameter to calculate the
route.
For each cost attribute that is accumulated, a Total_[Impedance] property
is added to the routes that are output by the solver.
Use
Hierarchy in Analysis (optional)
· Checked—Use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Using a hierarchy
results in the solver preferring higher-order edges to lower-order edges.
Hierarchical solves are faster, and they can be used to simulate the preference
of a driver who chooses to travel on freeways over local roads when
possible—even if that means a longer trip. This option is enabled only if the
input network dataset has a hierarchy attribute.
· Unchecked—Do not use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Not using a
hierarchy yields a service area measured along all edges of the network dataset
regardless of hierarchy level.
The parameter is disabled if a hierarchy attribute is not defined on the
network dataset used to perform the analysis.
Line Type
(optional)
Specifies the type of lines to be generated based on the service area
analysis. Selecting the True Lines or True lines with measures option for large
service areas will increase the amount of memory consumed by the analysis.
· NO_LINES—Do not generate lines. This is the default.
· TRUE_LINES—Lines are generated without measures.
· TRUE_LINES_WITH_MEASURES—Lines are generated with measures. The measure
values are generated based on the impedance value on each end of the edge with
the intermediate vertices interpolated. Do not use this option if faster
performance is desired.
Overlap
Lines (optional)
Determines if overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines
are computed.
· Checked—Include a separate line feature for each facility when the
facilities have service area lines that are coincident.
· Unchecked—Include each service area line at most once and associate it
with its closest (least impedance) facility.
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
6.
Time of Day (optional) الوقت من
اليوم (اختياري)
The time to depart from
or arrive at the facilities of the service area layer. The interpretation of
this value as a depart or arrive time depends on whether travel is away from or
toward the facilities.
وقت المغادرة أو الوصول إلى مرافق طبقة منطقة
الخدمة. يعتمد تفسير هذه القيمة كوقت مغادرة أو وصول على ما إذا كان السفر بعيدًا
عن المرافق أو باتجاهها.
• يمثل وقت المغادرة إذا
تم ضبط "السفر من أو إلى" على TRAVEL_FROM.
• يمثل وقت الوصول إذا تم
تعيين "السفر من أو إلى" على TRAVEL_TO.
إذا اخترت سمة المعاوقة المستندة إلى حركة المرور
، فسيتم إنشاء الحل وفقًا لظروف حركة المرور الديناميكية في الوقت المحدد هنا من
اليوم. يمكن تحديد التاريخ والوقت كـ 14/5/2012 10:30 صباحًا.
بدلاً من استخدام تاريخ معين ، يمكن تحديد يوم من
أيام الأسبوع باستخدام التواريخ التالية:
• اليوم - 12/30/1899
• الأحد - 12/31/1899
• الاثنين - 1/1/1900
• الثلاثاء - 1/2/1900
• الأربعاء - 1/3/1900
• الخميس - 1/4/1900
• الجمعة - 1/5/1900
• السبت - 1/6/1900
على سبيل المثال ، لتحديد أن السفر يجب أن يبدأ في
الساعة 5:00 مساءً. في يوم الثلاثاء ، حدد قيمة المعلمة كـ 1/2/1900 5:00 مساءً.
يسمح لك حل نفس التحليل بشكل متكرر ، ولكن
باستخدام قيم مختلفة للوقت من اليوم ، بمعرفة كيف يتغير مدى وصول المنشأة بمرور
الوقت. على سبيل المثال ، قد تبدأ منطقة الخدمة التي تبلغ مدتها خمس دقائق حول
محطة الإطفاء بشكل كبير في الصباح الباكر ، وتتقلص خلال ساعة الذروة الصباحية ،
وتنمو في وقت متأخر من الصباح ، وهكذا على مدار اليوم.
Accumulators
(optional)
A list of cost attributes to be accumulated during analysis. These
accumulation attributes are purely for reference; the solver only uses the cost
attribute specified by the Impedance Attribute parameter to calculate the
route.
For each cost attribute that is accumulated, a Total_[Impedance] property
is added to the routes that are output by the solver.
Use Hierarchy
in Analysis (optional)
· Checked—Use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Using a hierarchy
results in the solver preferring higher-order edges to lower-order edges.
Hierarchical solves are faster, and they can be used to simulate the preference
of a driver who chooses to travel on freeways over local roads when
possible—even if that means a longer trip. This option is enabled only if the
input network dataset has a hierarchy attribute.
· Unchecked—Do not use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Not using a
hierarchy yields a service area measured along all edges of the network dataset
regardless of hierarchy level.
The parameter is disabled if a hierarchy attribute is not defined on the
network dataset used to perform the analysis.
Line Type
(optional)
Specifies the type of lines to be generated based on the service area
analysis. Selecting the True Lines or True lines with measures option for large
service areas will increase the amount of memory consumed by the analysis.
· NO_LINES—Do not generate lines. This is the default.
· TRUE_LINES—Lines are generated without measures.
· TRUE_LINES_WITH_MEASURES—Lines are generated with measures. The measure
values are generated based on the impedance value on each end of the edge with
the intermediate vertices interpolated. Do not use this option if faster
performance is desired.
Overlap
Lines (optional)
Determines if overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines
are computed.
· Checked—Include a separate line feature for each facility when the
facilities have service area lines that are coincident.
· Unchecked—Include each service area line at most once and associate it
with its closest (least impedance) facility.
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon Nest
Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
7.
Accumulators (optional) مدخرات
(اختياري)
قائمة جدول التكلفة التي سيتم تجميعها أثناء
التحليل. جدول التراكم هذه للإشارة فقط ؛ يستخدم حلال فقط جدول التكلفة المحددة
بواسطة معلمة جدول المعاوقة لحساب المسار.
لكل جدول تكلفة يتم تجميعها ، تتم إضافة خاصية Total_
[معاوقة] إلى المسارات التي يتم إخراجها بواسطة المحلل.
Use
Hierarchy in Analysis (optional)
· Checked—Use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Using a hierarchy
results in the solver preferring higher-order edges to lower-order edges.
Hierarchical solves are faster, and they can be used to simulate the preference
of a driver who chooses to travel on freeways over local roads when
possible—even if that means a longer trip. This option is enabled only if the
input network dataset has a hierarchy attribute.
· Unchecked—Do not use the hierarchy attribute for the analysis. Not using a
hierarchy yields a service area measured along all edges of the network dataset
regardless of hierarchy level.
The parameter is disabled if a hierarchy attribute is not defined on the
network dataset used to perform the analysis.
Line Type
(optional)
Specifies the type of lines to be generated based on the service area
analysis. Selecting the True Lines or True lines with measures option for large
service areas will increase the amount of memory consumed by the analysis.
· NO_LINES—Do not generate lines. This is the default.
· TRUE_LINES—Lines are generated without measures.
· TRUE_LINES_WITH_MEASURES—Lines are generated with measures. The measure
values are generated based on the impedance value on each end of the edge with
the intermediate vertices interpolated. Do not use this option if faster
performance is desired.
Overlap
Lines (optional)
Determines if overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines
are computed.
· Checked—Include a separate line feature for each facility when the
facilities have service area lines that are coincident.
· Unchecked—Include each service area line at most once and associate it
with its closest (least impedance) facility.
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For instance,
If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute service area
polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area polygon. Use this
option if you want to find the entire area from the facility to the break for
each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
8.
Use Hierarchy in Analysis (optional) استخدام التسلسل الهرمي في التحليل (اختياري)
The parameter is
disabled if a hierarchy attribute is not defined on the network dataset used to
perform the analysis.
• تم التحديد - استخدم جدول التدرج الهرمي
للتحليل. يؤدي استخدام التسلسل الهرمي إلى تفضيل الحلول للحواف ذات الترتيب الأعلى
على الحواف ذات الترتيب الأدنى. تكون الحلول الهرمية أسرع ، ويمكن استخدامها
لمحاكاة تفضيل السائق الذي يختار السفر على الطرق السريعة عبر الطرق المحلية عندما
يكون ذلك ممكنًا - حتى لو كان ذلك يعني رحلة أطول. يتم تمكين هذا الخيار فقط إذا
كانت مجموعة بيانات شبكة الإدخال تحتوي على سمة التدرج الهرمي.
• غير محدد - لا تستخدم جدول
التدرج الهرمي للتحليل. ينتج عن عدم استخدام التسلسل الهرمي منطقة خدمة يتم قياسها
على طول جميع حواف مجموعة بيانات الشبكة بغض النظر عن مستوى التدرج الهرمي.
يتم تعطيل المعلمة إذا لم يتم تحديد جدول التدرج
الهرمي في مجموعة بيانات الشبكة المستخدمة لإجراء التحليل.
Line Type
(optional)
Specifies the type of lines to be generated based on the service area
analysis. Selecting the True Lines or True lines with measures option for large
service areas will increase the amount of memory consumed by the analysis.
· NO_LINES—Do not generate lines. This is the default.
· TRUE_LINES—Lines are generated without measures.
· TRUE_LINES_WITH_MEASURES—Lines are generated with measures. The measure
values are generated based on the impedance value on each end of the edge with
the intermediate vertices interpolated. Do not use this option if faster
performance is desired.
Overlap
Lines (optional)
Determines if overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines
are computed.
· Checked—Include a separate line feature for each facility when the
facilities have service area lines that are coincident.
· Unchecked—Include each service area line at most once and associate it
with its closest (least impedance) facility.
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be included
in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons or are
inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while creating a
drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and rails, you
should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so as to
correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
9.
Line Type (optional) نوع الخط
(اختياري)
Specifies the type of
lines to be generated based on the service area analysis. Selecting the True
Lines or True lines with measures option for large service areas will increase
the amount of memory consumed by the analysis.
يحدد نوع الخطوط التي سيتم إنشاؤها بناءً على
تحليل منطقة الخدمة. سيؤدي تحديد الخيار True Lines أو True lines with Measures (خطوط حقيقية) لمناطق الخدمة الكبيرة إلى زيادة مقدار الذاكرة
التي يستهلكها التحليل.
• NO_LINES - لا تنشئ خطوطًا. هذا هو الافتراضي.
• TRUE_LINES - يتم إنشاء الخطوط بدون مقاييس.
• TRUE_LINES_WITH_MEASURES - يتم إنشاء خطوط مع القياسات. يتم إنشاء قيم القياس بناءً على
قيمة المعاوقة على كل طرف من أطراف الحافة مع تقريب الرؤوس الوسيطة. لا تستخدم هذا
الخيار إذا كنت ترغب في أداء أسرع.
Overlap
Lines (optional)
Determines if overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines
are computed.
· Checked—Include a separate line feature for each facility when the
facilities have service area lines that are coincident.
· Unchecked—Include each service area line at most once and associate it
with its closest (least impedance) facility.
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
10.
Overlap Lines (optional) خطوط
متراكبة (اختياري)
Determines if
overlapping lines are generated when the service area lines are computed.
تحدد ما إذا كانت الأسطر المتداخلة قد تم إنشاؤها
عند حساب خطوط منطقة الخدمة.
• تم التحديد - قم بتضمين
ميزة خط منفصلة لكل منشأة عندما يكون للمنشآت خطوط منطقة خدمة متطابقة.
• غير محدد - قم بتضمين
كل خط منطقة خدمة مرة واحدة على الأكثر واربطه بأقرب مرفق (أقل مقاومة).
Split
Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional)
· Checked—Split every line between two breaks into two lines, each lying
within its break. This is useful if you want to symbolize the service area
lines by break. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked for optimal performance.
· Unchecked—The lines are not split at the boundaries of the breaks. This is
the default.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and rails,
you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so as to
correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
11.
Split Lines when They Cross a Service Area Break (optional) انقسام الخطوط عند عبورها إحدى استراحات منطقة الخدمة
(اختياري)
• تم التحديد - قم بتقسيم
كل سطر بين قسمين إلى سطرين ، يقع كل منهما داخل فاصل. يكون هذا مفيدًا إذا كنت
تريد ترميز خطوط منطقة الخدمة بفاصل. خلاف ذلك ، اترك هذا الخيار بدون تحديد
للحصول على الأداء الأمثل.
• لم يتم تحديده - لم يتم
تقسيم الأسطر عند حدود الفواصل. هذا هو الافتراضي.
Include
Network Source Fields in Lines (optional)
· Checked—Add the SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition, and ToPosition fields
to the service area lines to hold information about the underlying source
features traversed during the analysis. This can be useful to join the results
of the service area lines to the original source data.
· Unchecked—Do not add the source fields (SourceID, SourceOID, FromPosition,
and ToPosition) to the service area lines.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
12.
Include Network Source Fields in Lines (optional) تضمين حقول مصدر الشبكة في سطور (اختياري)
• تم التحديد - أضف حقول SourceID و SourceOID و FromPosition و ToPosition إلى خطوط منطقة الخدمة
للاحتفاظ بمعلومات حول ميزات المصدر الأساسية التي تم اجتيازها أثناء التحليل. قد
يكون هذا مفيدًا لربط نتائج خطوط منطقة الخدمة ببيانات المصدر الأصلية.
• غير محدد — لا تقم
بإضافة حقول المصدر (معرف المصدر ، معرف المصدر ، من الموضع ، والموضع) إلى خطوط
منطقة الخدمة.
Polygon
Type (optional)
Specifies the type of polygons to be generated.
· SIMPLE_POLYS—Creates generalized polygons, which are generated quickly and
are fairly accurate, except on the fringes. This is the default.
· DETAILED_POLYS—Creates detailed polygons, which accurately model the
service area lines and may contain islands of unreached areas. This option is
slower than generating generalized polygons.
· NO_POLYS—Turns off polygon generation for the case in which only service
area lines are desired.
If your data is of an urban area with a gridlike network, the difference
between generalized and detailed polygons would be minimal. However, for
mountain and rural roads, the detailed polygons may present significantly more
accurate results than generalized polygons.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For instance,
If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute service area
polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area polygon. Use this
option if you want to find the entire area from the facility to the break for
each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
13.
Polygon Type (optional) نوع المضلع
(اختياري)
يحدد نوع المضلعات التي سيتم إنشاؤها.
• SIMPLE_POLYS - يُنشئ مضلعات معممة ، يتم إنشاؤها بسرعة ودقة إلى حد ما ،
باستثناء الهامش. هذا هو الافتراضي.
• DETAILED_POLYS - يُنشئ مضلعات تفصيلية ، تضع نموذجًا دقيقًا لخطوط منطقة الخدمة
وقد تحتوي على جزر من المناطق التي لم يتم الوصول إليها. هذا الخيار أبطأ من توليد
المضلعات المعممة.
• NO_POLYS - لإيقاف إنشاء المضلع للحالة التي تكون فيها خطوط منطقة الخدمة
مطلوبة فقط.
إذا كانت بياناتك من منطقة حضرية بشبكة شبيهة
بالشبكة ، فسيكون الفرق بين المضلعات المعممة والمفصلة ضئيلاً. ومع ذلك ، بالنسبة
للطرق الجبلية والريفية ، قد تقدم المضلعات التفصيلية نتائج أكثر دقة بشكل ملحوظ
من المضلعات المعممة.
Merge
Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional)
Specifies the options to merge polygons that share similar break values.
This option is applicable only when generating polygons for multiple
facilities.
· NO_MERGE—Creates individual polygons for each facility. The polygons can
overlap each other.
· NO_OVERLAP—Creates individual polygons that are closest for each facility.
The polygons do not overlap each other.
· MERGE— Joins the polygons of multiple facilities that have the same break
value.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so as
to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
14.
Merge Polygons with Similar Ranges (optional) دمج المضلعات مع نطاقات مماثلة (اختياري)
يحدد خيارات دمج المضلعات التي تشترك في قيم فاصلة
مماثلة. هذا الخيار قابل للتطبيق فقط عند إنشاء مضلعات لمنشآت متعددة.
• NO_MERGE - يُنشئ مضلعات فردية لكل منشأة. يمكن أن تتداخل المضلعات مع
بعضها البعض.
• NO_OVERLAP - يُنشئ المضلعات الفردية الأقرب لكل منشأة. لا تتداخل المضلعات
مع بعضها البعض.
• دمج - ينضم إلى
المضلعات في منشآت متعددة لها نفس قيمة الفاصل.
Polygon
Nest Option (optional)
Specifies the option to create concentric service area polygons as disks
or rings. This option is applicable only when multiple break values are
specified for the facilities.
· RINGS—Do not include the area of the smaller breaks. This creates polygons
going between consecutive breaks. Use this option if you want to find the area
from one break to another.
· DISKS— Creates the polygons going from the facility to the break. For
instance, If you create 5- and 10-minute service areas, then the 10-minute
service area polygon will include the area under the 5-minute service area
polygon. Use this option if you want to find the entire area from the facility
to the break for each break.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
15.
Polygon Nest Option (optional) خيار
عش المضلع (اختياري)
يحدد خيار إنشاء مضلعات منطقة خدمة متحدة المركز
كأقراص أو حلقات. هذا الخيار قابل للتطبيق فقط عندما يتم تحديد قيم فاصلة متعددة
للمرافق.
• حلقات - لا تقم بتضمين
منطقة الفواصل الأصغر. يؤدي هذا إلى إنشاء مضلعات تتنقل بين فواصل متتالية. استخدم
هذا الخيار إذا كنت تريد العثور على المنطقة من فاصل إلى آخر.
• الأقراص - تنشئ
المضلعات التي تنتقل من المنشأة إلى الفاصل. على سبيل المثال ، إذا قمت بإنشاء
مناطق خدمة مدتها 5 دقائق و 10 دقائق ، فسيتضمن مضلع منطقة الخدمة لمدة 10 دقائق
المنطقة الواقعة أسفل مضلع منطقة الخدمة لمدة 5 دقائق. استخدم هذا الخيار إذا كنت
تريد العثور على المنطقة بأكملها من المنشأة إلى الاستراحة لكل فاصل.
Exclude
Sources from Polygon Generation (optional)
Specifies the list of network sources to be excluded when generating the
polygons. The geometry of traversed elements from the excluded sources will be
omitted from all polygons.
This is useful if you have some network sources that you don't want to be
included in the polygon generation because they create less accurate polygons
or are inconsequential for the service area analysis. For example, while
creating a drive time service area in a multimodal network of streets and
rails, you should choose to exclude the rail lines from polygon generation so
as to correctly model where a vehicle could travel.
Excluding a network source from service area polygons does not prevent
those sources from being traversed. Excluding sources from service area
polygons only influences the polygon shape of the service areas. If you want to
prevent traversal of a given network source, you must create an appropriate
restriction when defining your network dataset.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
16.
Exclude Sources from Polygon Generation (optional) استبعاد المصادر من إنشاء المضلع (اختياري)
يحدد قائمة مصادر الشبكة التي سيتم استبعادها عند
إنشاء المضلعات. سيتم حذف هندسة العناصر التي تم اجتيازها من المصادر المستبعدة من
كافة المضلعات.
يكون هذا مفيدًا إذا كان لديك بعض مصادر الشبكة
التي لا تريد تضمينها في إنشاء المضلع لأنها تنشئ مضلعات أقل دقة أو غير مهمة
لتحليل منطقة الخدمة. على سبيل المثال ، أثناء إنشاء منطقة خدمة وقت القيادة في
شبكة متعددة الوسائط من الشوارع والقضبان ، يجب عليك اختيار استبعاد خطوط السكك
الحديدية من إنشاء المضلع حتى تتمكن من وضع نموذج صحيح للمكان الذي يمكن للمركبة
أن تسير فيه.
لا يؤدي استبعاد مصدر شبكة من مضلعات منطقة الخدمة
إلى منع اجتياز هذه المصادر. يؤثر استبعاد المصادر من مضلعات منطقة الخدمة فقط على
شكل المضلع لمناطق الخدمة. إذا كنت تريد منع اجتياز مصدر شبكة معين ، فيجب عليك
إنشاء قيد مناسب عند تحديد مجموعة بيانات الشبكة الخاصة بك.
Trim
Polygons (optional)
· Checked—Trims the polygons containing the edges at the periphery of the
service area to be within the specified distance of these outer edges. This is
useful if the network is very sparse and you don't want the service area to
cover large areas where there are no features.
· Unchecked—Do not trim polygons.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
17.
Trim Polygons (optional) قطع
المضلعات (اختياري)
• تم التحديد - يقوم
بتشذيب المضلعات التي تحتوي على الحواف عند محيط منطقة الخدمة لتكون ضمن المسافة
المحددة لهذه الحواف الخارجية. يكون هذا مفيدًا إذا كانت الشبكة متفرقة جدًا ولا
تريد أن تغطي منطقة الخدمة مناطق كبيرة لا توجد بها ميزات.
• غير محدد - لا تقطع
المضلعات.
Polygon
Trim (optional)
Specifies the distance within which the service area polygons are trimmed.
The parameter includes a value and units for the distance. The default value is
100 meters.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
18.
Polygon Trim (optional) تقليم مضلع
(اختياري)
يحدد المسافة التي يتم قطع مضلعات منطقة الخدمة
ضمنها. تتضمن المعلمة قيمة ووحدات للمسافة. القيمة الافتراضية هي 100 متر.
U-Turn
Policy (optional)
The U-Turn policy at junctions. Allowing U-turns implies the solver can
turn around at a junction and double back on the same street. Given that
junctions represent street intersections and dead ends, different vehicles may
be able to turn around at some junctions but not at others—it depends on
whether the junction represents an intersection or dead end. To accommodate
this, the U-turn policy parameter is implicitly specified by how many edges
connect to the junction, which is known as junction valency. The acceptable
values for this parameter are listed below; each is followed by a description
of its meaning in terms of junction valency.
· ALLOW_UTURNS—U-turns are permitted at junctions with any number of
connected edges. This is the default value.
· NO_UTURNS—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, regardless of junction
valency. Note, however, that U-turns are still permitted at network locations
even when this setting is chosen; however, you can set the individual network
location's CurbApproach property to prohibit U-turns there as well.
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at all junctions, except those
that have only one adjacent edge (a dead end).
· ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY—U-turns are prohibited at junctions
where exactly two adjacent edges meet but are permitted at intersections
(junctions with three or more adjacent edges) and dead ends (junctions with
exactly one adjacent edge). Often, networks have extraneous junctions in the
middle of road segments. This option prevents vehicles from making U-turns at
these locations.
If you need a more precisely defined U-turn policy, consider adding a
global turn delay evaluator to a network cost attribute, or adjusting its
settings if one exists, and pay particular attention to the configuration of
reverse turns. Also, look at setting the CurbApproach property of your network
locations.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
19.
U-Turn Policy (optional) السياسة
(اختياري)
سياسة U-Turn عند
التقاطعات. يعني السماح بالدوران على شكل حرف U أنه
يمكن للحل أن يستدير عند تقاطع طرق ويتضاعف مرة أخرى في نفس الشارع. نظرًا لأن
التقاطعات تمثل تقاطعات الشوارع والطرق المسدودة ، فقد تتمكن المركبات المختلفة من
الالتفاف عند بعض التقاطعات ولكن ليس عند البعض الآخر - يعتمد ذلك على ما إذا كان
التقاطع يمثل تقاطعًا أو طريقًا مسدودًا. لاستيعاب ذلك ، يتم تحديد معلمة نهج U-turn
ضمنيًا من خلال عدد الحواف المتصلة بالوصلة ، والتي تُعرف باسم تكافؤ الوصلة.
القيم المقبولة لهذه المعلمة مذكورة أدناه ؛ يتبع كل منها وصف لمعناها من حيث
تكافؤ الوصلات.
• ALLOW_UTURNS - يُسمح بالدوران على شكل حرف U عند
التقاطعات مع أي عدد من الحواف المتصلة. هذه هي القيمة الافتراضية.
• NO_UTURNS - يحظر الدوران U في
جميع التقاطعات ، بغض النظر عن تكافؤ الوصلات. لاحظ ، مع ذلك ، أن المنعطفات U لا
يزال مسموحًا بها في مواقع الشبكة حتى عند اختيار هذا الإعداد ؛ ومع ذلك ، يمكنك
تعيين خاصية CurbApproach الخاصة بموقع الشبكة
الفردي لمنع انعطاف U هناك أيضًا.
• ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_ONLY - يحظر الدوران للخلف في جميع التقاطعات ، باستثناء تلك التي لها
حافة مجاورة واحدة (طريق مسدود).
• ALLOW_DEAD_ENDS_AND_INTERSECTIONS_ONLY - يُحظر استخدام
المنعطفات على شكل حرف U عند التقاطعات حيث تلتقي
حافتان متجاورتان تمامًا ولكن يُسمح بها عند التقاطعات (التقاطعات ذات ثلاثة حواف
متجاورة أو أكثر) والنهايات المسدودة (التقاطعات ذات حافة متجاورة واحدة بالضبط).
غالبًا ما تحتوي الشبكات على تقاطعات خارجية في منتصف أجزاء الطريق. يمنع هذا
الخيار المركبات من الدوران للخلف في هذه المواقع.
إذا كنت بحاجة إلى سياسة U-turn محددة
بشكل أكثر دقة ، ففكر في إضافة مقيِّم لتأخير الانعطاف العالمي إلى سمة تكلفة
الشبكة ، أو تعديل إعداداتها إن وجدت ، وإيلاء اهتمام خاص لتكوين المنعطفات
العكسية. انظر أيضًا إلى إعداد خاصية CurbApproach
لمواقع الشبكة الخاصة بك.
Restrictions
(optional)
A list of restriction attributes to apply during the analysis.
20.
Restrictions (optional) قيود
(اختياري)
A list of restriction attributes
to apply during the analysis.
قائمة جدول التقييد المطلوب تطبيقها أثناء التحليل.
اليك صفحه ومجموعة على الفيس بوك لتعلم أكثر بما يخص نظم المعلومات الجغرافية (GIS) و برنامج ArcGIS Pro من خلال هذه الروابط:




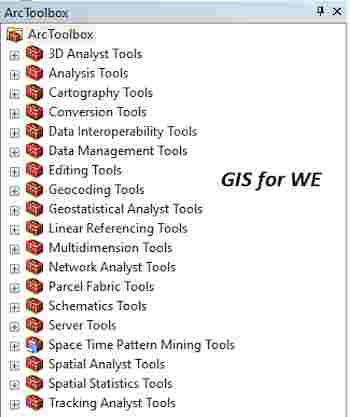

تعليقات
إرسال تعليق